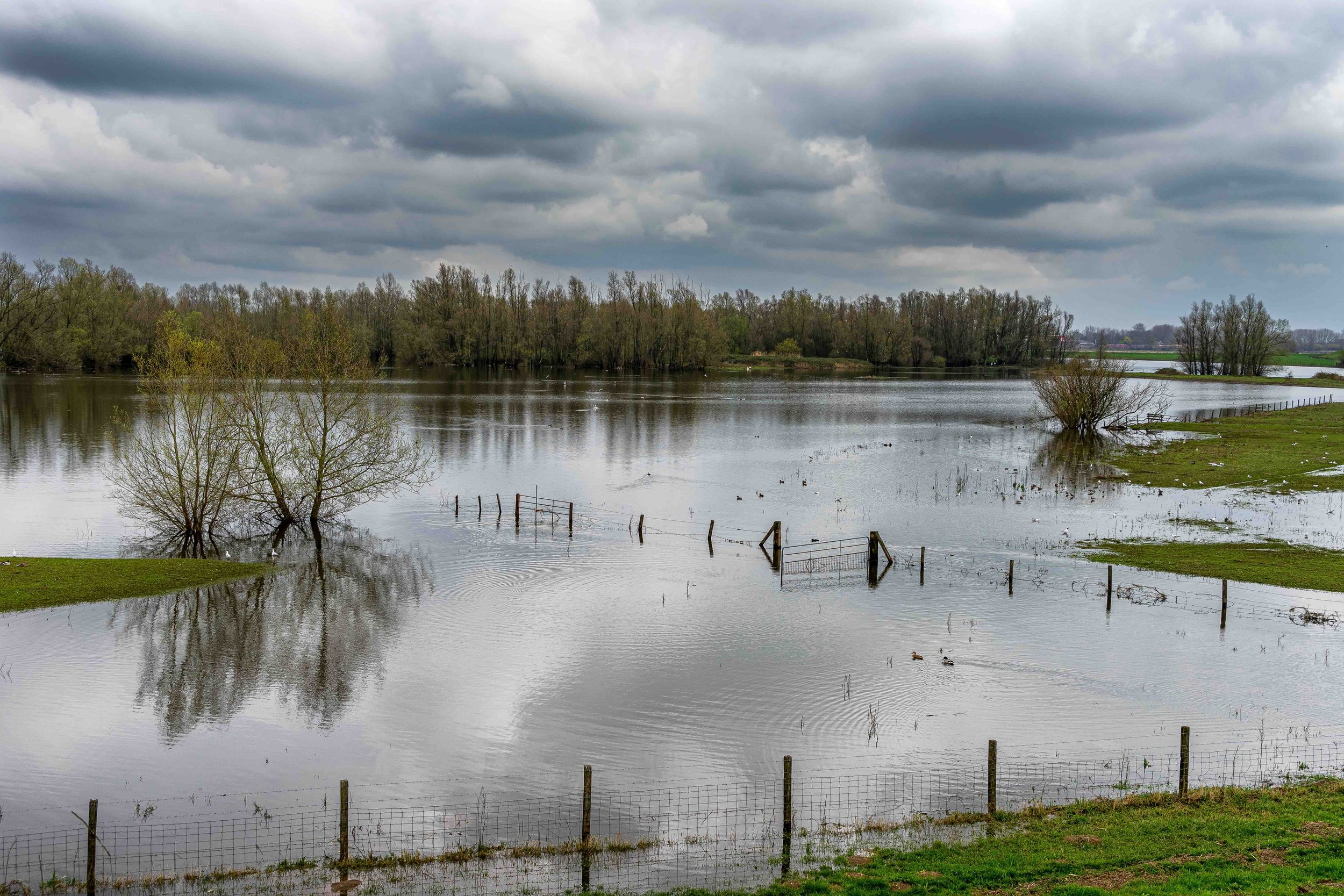
Floods and Drought Research
/The UK government is investing £38 million in advanced research infrastructure to improve the understanding and prediction of floods and droughts. The project will utilize cutting-edge technology to monitor and analyze key aspects of the water environment.
Digital instruments will be installed along major UK rivers to continuously collect real-time data on evaporation, soil moisture, weather conditions, groundwater levels, and river flows. Advanced computer models will then process this data to provide accurate forecasts.
The Flood and Droughts Research Infrastructure (FDRI) will create a detailed data network through "outdoor labs" on rivers such as the Severn, Chess, and Tweed. This network is designed to enhance forecasting capabilities and develop new technologies. By integrating and analyzing the collected data, the project aims to improve the prediction and management of extreme weather events, ultimately boosting protection for communities and infrastructure.
Read full article